The food service industry is one of its main contributors, with plate waste, discarded kitchen trimmings and expired ingredients all playing a significant role.
An Introduction to Closed Loop Cooking
Looking for an effective way to minimise food waste?
A guide for food service businesses.


Food waste is a global issue that has serious implications on the environment.
So what can food service businesses do to improve the situation?
Introducing closed loop cooking – a highly-efficient system for reducing food waste, boosting profits and inspiring more creativity in the kitchen.

This guide provides a comprehensive understanding of closed loop cooking and its practical applications in the food service industry.

DEFINITION
What is closed loop cooking?
Closed loop cooking is an approach aimed at minimising waste throughout the entire food preparation process. It involves adopting sustainable practices at every stage, from sourcing ingredients to cooking, serving and handling leftovers.
How does it work?
This concept emphasises a holistic view of the cooking process, encouraging chefs to consider the environmental impact of their choices, including strategies such as:
Mindful ingredient selection
Efficient use of resources
Creative ways of repurposing food scraps

Why should we use it?
Implementing a closed loop cooking system is a powerful way of fostering a collective effort to minimise food waste and building a more sustainable culinary community.

FOOD WASTE
Why is zero food waste important?
As key players in the supply chain, food service businesses have the power to reduce waste generation, leading to positive impacts on the planet and on their bottom line.
ZERO FOOD WASTE
The profitability aspect
Waste reduction can also boost business profitability. Adopting sustainable practices like using every part of an ingredient, implementing portion control, and creatively repurposing leftovers can lead to cost savings through efficient resource utilisation and minimised disposal expenses.
What’s more, today’s customers increasingly support businesses that prioritise sustainability, so focusing on zero waste can lead to greater customer loyalty and an enhanced brand image.


ZERO FOOD WASTE
The environmental impact
The huge amounts of food waste ending up in landfills contribute to greenhouse gas emissions and climate change, significantly damaging the natural environment.
The food service industry can actively contribute to minimising its ecological footprint by aiming for zero waste with responsible sourcing, portion control and innovative cooking techniques.
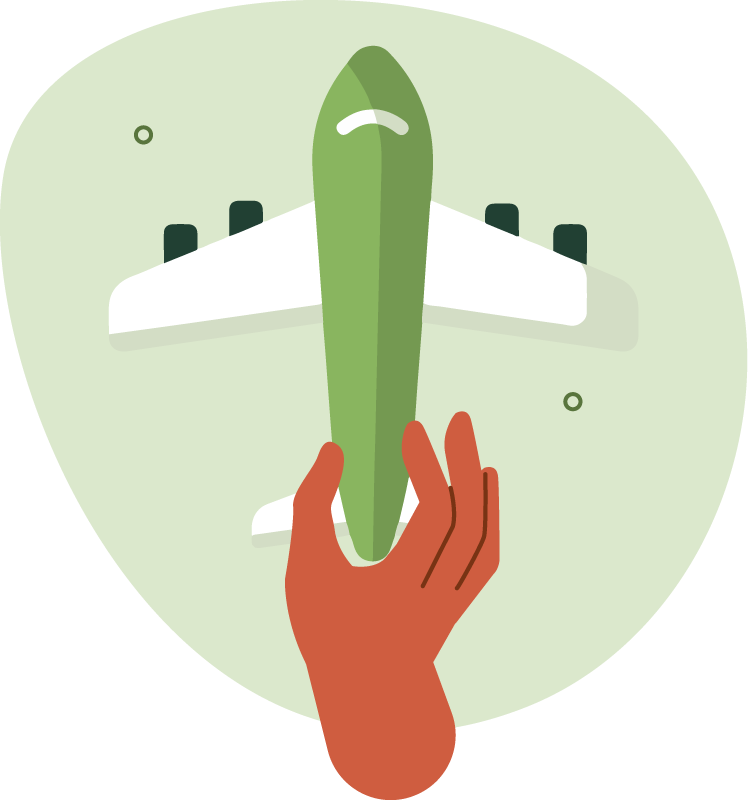

DID YOU KNOW?
A study by the World Wildlife Fund found that food waste including transportation accounts for about 10% of global greenhouse gas emissions. This is the equivalent of almost five times the total emissions from the Aviation sector.

KEY PRINCIPLES
A breakdown of closed loop kitchen systems
Closed loop cooking practices – also known as zero-waste or root-to-stem cooking – involve minimising food waste by utilising ingredients in their entirety and in various ways throughout the cooking process.
This approach is environmentally conscious and promotes sustainability in the kitchen and across menu planning.
So what are the key principles of closed loop cooking?
KEY PRINCIPLE #1
Sourcing sustainable ingredients
PRO TIP
Local collaboration
Maintain open communication with your local suppliers, arranging periodic visits to build a stronger partnership. Take your kitchen team along too – this will engage them further in your sustainability mission.
KEY PRINCIPLE #2
Minimising kitchen scraps
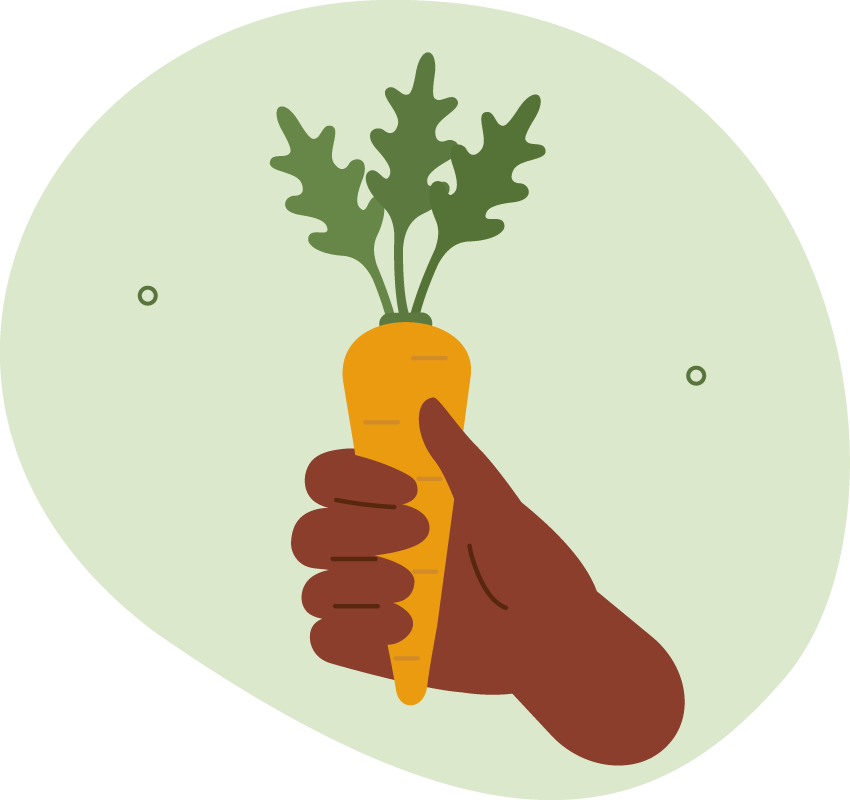

TRY THIS
Utilising a whole carrot in a dish
Mix whipped feta, honey and thyme nut granola, with roast carrot; or make pickled carrot, crispy carrot skins and carrot top salsa verde, or turn carrot and other vegetable peels into chips.
KEY PRINCIPLE #3
Limiting ingredients in menu planning

TRY THIS
Using versatile ingredients
Using ingredients across multiple dishes further optimises efficiency and minimises waste in food preparation. Roasted courgette, aubergines, and butternut squash could be featured on a flatbread, but they could also be used in a grain salad with couscous or in an aromatic curry finished with coconut milk and toasted chickpeas.
KEY PRINCIPLE #5
Introducing diverse textures and flavours
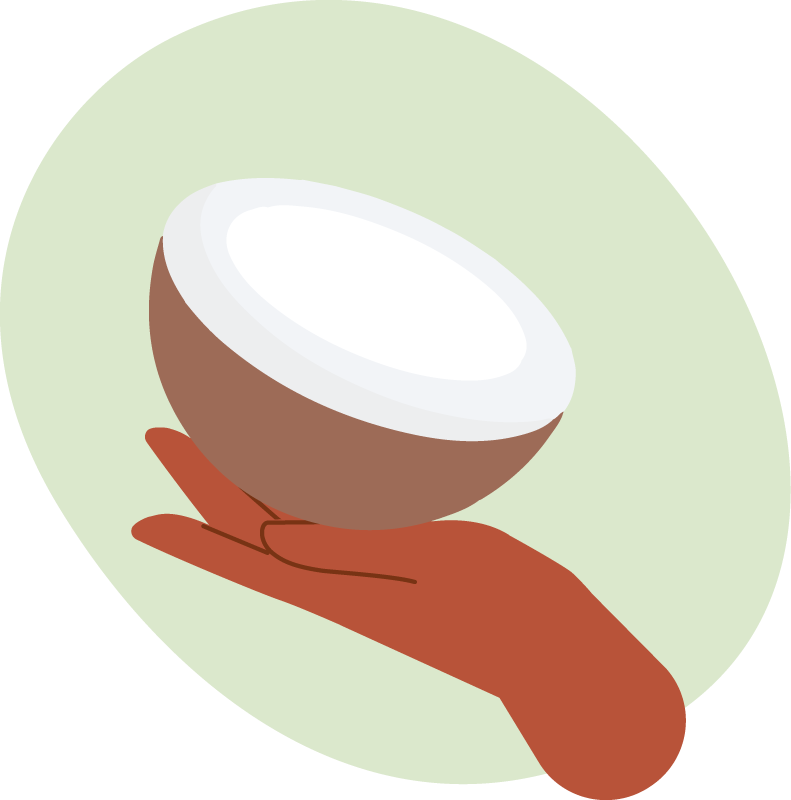

TRY THIS
Coconuts
By incorporating toasted desiccated coconut for savoury nuttiness, coconut flesh for sweetness, and coconut milk or water for a mild balance of both sweet and savoury notes, chefs can create dishes that offer a delightful interplay of flavours.

The key benefits of closed loop cooking
Adopting a closed loop cooking system can have significantly positive effects on the environment, business profitability and customer satisfaction.
Reduced food waste
According to the Food and Agriculture Organisation of the United Nations (FAO), approximately one third of all food produced for human consumption is lost or wasted globally each year. Closed loop cooking practices directly address this issue by minimising food waste at the source.
Less environmental impact
Reducing food waste minimises the greenhouse gas emissions associated with decomposing organic matter in landfills and excessive water usage. With its emphasis on local, seasonal and whole ingredient use, closed loop cooking can contribute to reducing the carbon footprint associated with food production, transportation and waste management.
Increased sustainability
Focusing on local and seasonal ingredients supports biodiversity and encourages the use of a variety of crops, helping to preserve different plant species. Closed loop cooking practices also align with sustainable farming methods, promoting healthier soil and ecosystems.
Better community engagement
Closed loop cooking often involves building relationships with local farmers and producers to secure fresh, seasonal produce without the carbon footprint of buying from overseas. This fosters a sense of community and supports local economies.
More cost savings
A study by the Waste and Resources Action Program (WRAP) suggests that reducing food waste can lead to substantial cost savings for businesses, with a potential return on investment within a short timeframe. By minimising waste in the purchasing and use of ingredients, as well as streamlining of menus, businesses can reduce operational costs over time and save money.
Enhanced consumer perception
As awareness of environmental issues grows, customers are becoming more inclined to support restaurants that prioritise zero-waste practices. Transparent communication about sustainable practices such as closed-loop cooking can enhance a business’ reputation and help build brand loyalty.

DID YOU KNOW?
A Nielsen survey found that 73% of consumers are willing to pay more for products made with sustainable and locally sourced ingredients.
ESG impact
Introducing closed loop cooking into your business will contribute greatly towards ESG, which also showcases a commitment to sustainable governance.

Environmental
Closed loop cooking will help reduce food waste, thereby contributing to the ‘environmental’ pillar of ESG.

Social
Socially responsible businesses demonstrating a commitment to minimising food waste and attracting conscious consumers serve to enhance the ‘social’ pillar of ESG.

Governance
Financial stability resulting from waste reduction positively contributes to the ‘governance’ pillar of ESG. Improved financial performance enables businesses to invest more in socially responsible initiatives.

ESG IMPACT
How to implement a closed loop cooking system
For a successful closed loop cooking system, you need a clear picture of your business’ current situation and future goals, as well as an efficient approach to stock taking and menu engineering. It’s also essential to get all staff on board and strive for continuous improvement.
Here’s how to do it in 7 key steps.
STEP 1
Conduct a thorough assessment
Focus on your menu offerings and compare these to your sales data, identifying the most popular and profitable dishes.
Measure food waste at all stages, including preparation, cooking, serving and customer leftovers. Using smart food waste tracking technologies like DigiTally can simplify this by identifying and measuring your waste streams and analysing the reasons behind them.
STEP 2
Set goals and metrics
- Your gross profit % – the profit achieved after costs are deducted from sales.
- Your days on hand – how many days it takes to use up your stock (for a food business, it should be less than 7 days)
- Your food waste in grams per cover – including uneaten food returned by customers (plate waste).
STEP 3
Optimise your menu
STEP 4
Build supplier relationships
Collaborate closely to optimise ordering quantities and frequencies based on predicted demand.
STEP 5
Manage your inventory
STEP 6
Train kitchen staff
STEP 7
Monitor for continuous improvement

Remember: The “carrot and stick” approach won’t work – there is no “stick” with food waste.
You’ll only risk losing team buy-in.
Instead, raise awareness of the positive outcomes you’re aiming for and offer incentives to reward star team players. Carrots all the way!
Wrapping up
The positive impacts of closed loop cooking are threefold: environmental, financial, and reputational.
While the journey requires an investment of time and commitment, the potential rewards are transformative.
Food service businesses that embrace these sustainable practices have the potential to become leaders in the industry by making eco-conscious consumers happy, protecting the planet and driving profits.
In an era of increasing environmental urgency, there has never been a better time to join the closed loop cooking revolution.